Tooth #2, also known as the lateral incisor, is one of the most important teeth in the dental arch. Adults have a total of four Tooth #2s, including two in the upper jaw and two in the lower jaw. They are located immediately in the front of the dental arch, adjacent to the central incisor (Tooth #1) and the canine (Tooth #3), playing a pivotal role in both chewing function and smile aesthetics.
In terms of shape, Tooth #2 is characteristically small and tapered, with a slender crown and a fairly sharp biting edge, helping to aid in biting and tearing food. Although not as large as the central incisor, they create balance and harmony for the entire dental arch.
In terms of structure, Tooth #2 consists of several parts similar to other teeth:
-
Crown: the part visible above the gum, easily observed and subject to external forces.
-
Neck: the transition area between the crown and the root, which is also the junction with the gum.
-
Root: the part located deep within the jawbone, which anchors the tooth, only clearly visible on X-ray films.
-
Tissue Layers: including enamel (the hard protective outer layer), dentin (located inside, sensitive to stimuli), pulp (containing blood vessels and nerves that nourish the tooth), and cementum (covering the outside of the root, helping to link with the periodontal ligament).
The function of Tooth #2 is remarkable despite its modest size. They not only assist in biting and cutting food but also play a crucial role in speech articulation, helping to produce precise fricative and plosive sounds. Aesthetically, Tooth #2 is located right in the center of the smile, determining the harmony of the face. When lost, the resulting gap causes imbalance, directly affecting confidence in communication.
Causes of Missing Tooth #2
Tooth #2 loss can result from various causes, including pathological factors, trauma, or congenital conditions. Understanding the cause helps the doctor propose the most appropriate treatment and restoration method, and also helps the customer proactively prevent it.
Severe Tooth Decay and Pulpitis
The lateral incisor is small and has thin enamel, making it highly susceptible to bacterial attack and rapid decay spread. If detected late or not treated promptly, decay can penetrate deep into the pulp, causing inflammation, necrosis, which weakens the tooth and necessitates extraction. In fact, many cases of Tooth #2 loss in adults stem from advanced decay, originating from improper oral hygiene habits and a high-sugar diet.
Accidents and Trauma to the Frontal Teeth Area
Tooth #2 is located in the front of the dental arch, making it highly vulnerable to injury from strong impacts. Common situations include falls, traffic accidents, sports injuries, or collisions in daily life. When the tooth is completely fractured or knocked out of the jawbone, preservation is often not feasible, requiring restoration using a false tooth method or Implant.
Periodontal Disease
Periodontitis is a leading cause of tooth loss in adults, and the lateral incisor is no exception. When the gum tissue and alveolar bone are chronically inflamed, the tooth root loses its stable anchor point, causing the tooth to loosen and easily fall out. Since Tooth #2 is small and has a slender root, the ability to retain the natural tooth is low when periodontitis is advanced.
Congenital Factors
A small percentage of people are congenitally missing Tooth #2 or have teeth that erupt abnormally. The cause is often genetic factors or disorders in the tooth germ formation process. This condition not only causes aesthetic loss but also affects the bite, easily causing other teeth to shift to compensate for the gap. For these cases, early false tooth restoration or Implant placement is the solution to ensure aesthetics and function.
Consequences of Missing Tooth #2
Missing Tooth #2 not only creates a gap in the dental arch but also leads to many serious consequences for aesthetics, speech, and oral health. If not restored promptly, these effects become increasingly apparent and difficult to remedy.
Impact on Smile Aesthetics
Tooth #2 is centrally located, right in the aesthetic zone of the smile. When lost, the gap is easily noticeable, making the smile look unbalanced, the face appear older, and less natural. Especially for those whose jobs require frequent communication, missing Tooth #2 can reduce self-confidence, directly affecting their personal image and social relationships.
Causes Difficulty in Speech Articulation
The lateral incisor plays an important role in articulating many fricative and plosive sounds. When Tooth #2 is lost, the airflow is not properly controlled, leading to incorrect or lisping speech. This often causes patients difficulty in communication, especially in academic, work environments, or situations requiring extensive speaking.
Affects Chewing Function
Although not subjected to strong chewing forces like molars, Tooth #2 still assists in the process of biting and tearing food. When this tooth is lost, the biting force decreases, and the patient has to concentrate force onto other teeth, causing bite imbalance and making adjacent teeth wear out faster. In the long run, this condition can lead to temporomandibular joint disorders, causing pain and difficulty when eating.
Jawbone Resorption and Bite Misalignment
A Tooth #2 gap that is not restored will lead to alveolar bone resorption over time. As the jawbone shrinks, the gums recede, making the face look sunken and aged. Furthermore, the adjacent Tooth #1 and Tooth #3 tend to tilt into the gap, causing bite misalignment, affecting the entire jaw structure. This is why future restoration becomes more complicated and expensive.
Restoration Solutions for Missing Tooth #2
When Tooth #2 is lost, early restoration is essential to maintain smile aesthetics, chewing function, and prevent jawbone resorption. Currently, there are three common methods applied: dental bridge, Implant placement, and removable dentures.
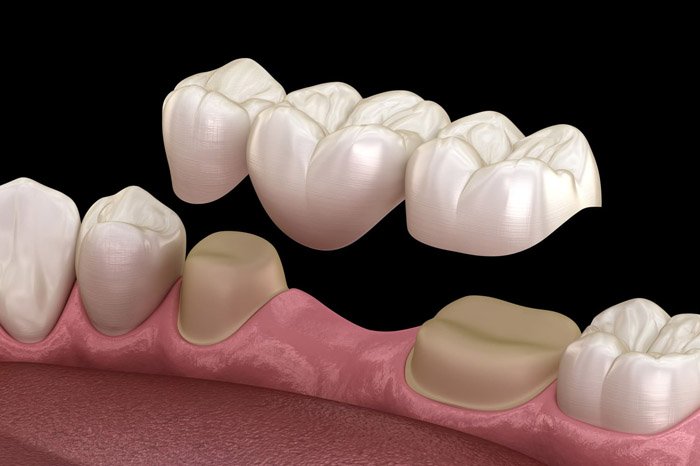
Dental Bridge
The dental bridge is a traditional method that uses the two adjacent teeth (Tooth #1 and Tooth #3) as abutments, then attaches a false tooth to replace Tooth #2. The advantage of a dental bridge is quick restoration time, lower cost compared to Implants, and it provides fairly high aesthetics. The patient can restore a natural smile in just a few days. However, the biggest drawback is that it requires grinding down two healthy natural teeth to serve as abutments, making them sensitive and weaker over time. Additionally, a dental bridge does not prevent jawbone resorption at the missing tooth site.
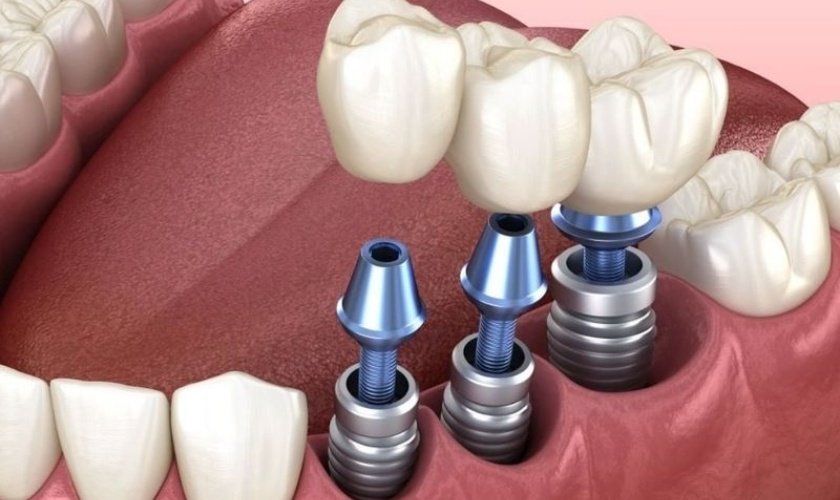
Dental Implant Placement
Dental Implant placement is the most modern and optimal solution today to replace a missing Tooth #2. The doctor places a titanium Implant post into the jawbone at the missing tooth location, then attaches a porcelain crown on top for complete restoration. The outstanding advantage of this method is its ability to recreate a tooth almost like a natural tooth, in both function and aesthetics. Implants have high durability, with a lifespan that can reach decades, or even permanently, with good care. Importantly, Implants also help prevent jawbone resorption—a problem that other methods do not solve. The only drawback is the higher cost compared to dental bridges or removable dentures, and it requires the jawbone to be in suitable condition for post placement.
Removable Dentures
Removable dentures are the most cost-effective option for people with missing Tooth #2. The doctor fabricates a false tooth made of plastic or combined with a metal framework to fit into the missing tooth gap. The advantage is low cost, ease of creation, suitable for those who do not yet have the financial means or cannot undergo Implant placement immediately.
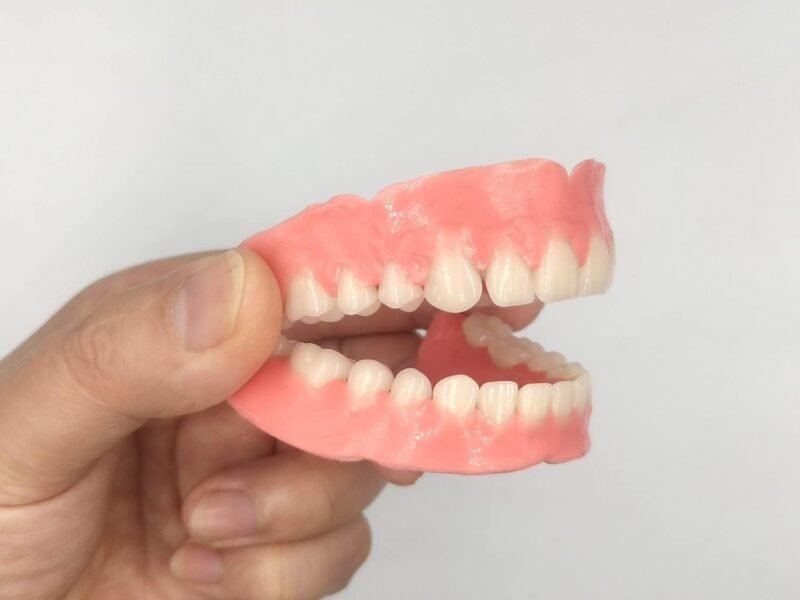
However, removable dentures have many limitations: aesthetics are not high, they feel bulky when chewing, they can loosen over time, and they do not prevent jawbone resorption. Typically, this is only a temporary solution before the patient decides on a fixed restoration method.
Each solution has its own pros and cons, and the doctor will advise the most suitable option based on the oral condition and financial capabilities. Among them, Implants are considered the optimal choice for missing Tooth #2, ensuring long-term aesthetics and maintaining jawbone health.
Cost of Tooth #2 Restoration
The cost of replacing Tooth #2 depends on the restoration method, the material used, and the individual patient’s oral condition. In reality, each technique has a different price range, suitable for varying needs and financial conditions.
-
Dental Bridge: This is a mid-range cost method, varying depending on the type of porcelain used. Common types include metal-fused porcelain, Titanium porcelain, all-porcelain Zirconia, or E.max. The price is usually lower than Implant placement, but the lifespan only lasts 7–10 years and it does not prevent jawbone resorption.
-
Dental Implant Placement: This is the highest cost method but provides optimal and long-lasting effectiveness. The price of an Implant depends on the type of post (Korean, American, German…), the accompanying porcelain crown, and the patient’s jawbone condition. In cases of bone loss, bone grafting is required before placement, which will increase the cost. The advantage is a lifespan that can exceed 20 years, even permanently, making it very economical in the long term.
-
Removable Dentures: This is the lowest-cost option, suitable for customers who want a temporary solution. However, aesthetics are limited, they can feel bulky when eating, and the lifespan is short. Often, after a period, the customer still has to switch to a dental bridge or Implant for a durable result.
In addition to the restoration method, the cost also depends on other factors such as:
-
The skill level and experience of the performing doctor.
-
Equipment and supporting technology at the dental clinic.
-
Warranty and post-operative care policy.
Thus, the cost of Tooth #2 restoration can range from low (removable dentures) to high (Implants), but the effectiveness and durability are directly proportional to the cost. To get an accurate price quote tailored to individual conditions, customers should visit a reputable dental clinic for a direct examination.
3C Dental Clinic – Reputable Address for Tooth #2 Placement
When restoring the lateral incisor, aesthetics and precision must be prioritized. Therefore, choosing a reputable dental clinic with a highly qualified team and modern technology is extremely important. At 3C Dental Clinic, we offer a comprehensive solution for customers with missing Tooth #2 thanks to superior advantages:
-
Highly Qualified Doctor Team: Doctors at3C Dental Clinic have many years of experience in the field of tooth restoration, especially dental Implants and aesthetic porcelain restoration.
-
Modern Equipment: Utilizing 3D diagnostic imaging technology, CT ConeBeam machine, and digital smile design software, ensuring the treatment process is accurate, safe, and highly effective.
-
Genuine Materials: All Implant posts and porcelain crowns are imported from reputable international brands, ensuring durability, aesthetics, and biological safety.
-
International Standard Treatment Procedure: Strictly adhering to sterilization regulations, with closed operating rooms, minimizing the risk of cross-contamination.
-
Reputable Care and Warranty Policy: Customers are monitored after treatment, provided with a long-term warranty, and instructed on proper oral hygiene.

3C Dental Clinic is committed to not only restoring a strong Tooth #2 but also providing a natural smile that harmonizes with the face. This is the factor that makes many customers trust and choose us when they need lateral incisor restoration.
Frequently Asked Questions About Missing Tooth #2
Missing Tooth #2 is a common condition, so customers often ask many questions related to restoration feasibility, pain level during treatment, or the effect on adjacent teeth. Below are the most common inquiries that Nha khoa 3C has compiled and answered.
Can a Tooth #2 that has been missing for many years be replaced?
It is absolutely possible to replace Tooth #2 even if it has been missing for many years. However, in cases of long-term tooth loss, the jawbone at that location is often severely resorbed, making the bone density and volume insufficient for Implant post placement. The solution is that the doctor will prescribe bone grafting or sinus lift (if necessary) before placing the Implant, which provides a solid foundation for the post. Therefore, early examination is always encouraged to make the restoration process easier, saving time and cost.
Is Implant placement for the lateral incisor (Tooth #2) painful?
With modern technology, Implant placement for Tooth #2 is virtually not as painful as many people worry. During the procedure, the doctor will apply local anesthesia, and the customer will be completely comfortable. After post placement, the area may be slightly sensitive or swollen for the first few days, but this condition will quickly subside if the doctor’s care instructions are followed. Compared to the long-term effectiveness that Implants provide, this discomfort is very minimal and completely controllable.
Does missing Tooth #2 affect Tooth #1 and Tooth #3?
Yes, it does. When Tooth #2 is lost, the adjacent Tooth #1 and Tooth #3 are directly affected. They tend to tilt into the gap, leading to bite misalignment, increasing the risk of enamel wear and periodontitis. If this situation persists, restoration will be more difficult, and it will also affect the aesthetic structure of the face. Therefore, doctors always recommend early restoration to protect overall oral health.
Missing Tooth #2 not only affects smile aesthetics but also causes difficulty in speech, chewing, and leads to jawbone resorption if not restored promptly. Modern solutions such as Dental Implant placement or a Dental Bridge effectively help restore the lateral incisor, maintaining confidence and oral health. 👉 Contact Nha khoa 3C now for an examination and consultation on the most suitable Tooth #2 replacement method for you.
